SAP HANA Backup
SAP HANA Persistence
To
ensure optimal performance, the SAP HANA database holds most of its data
in-memory. However, it still uses persistent storage to provide a fallback in
case of failure.
During
normal database operation, data
is automatically saved from memory to disk at regular savepoints. Additionally, all data changes
are recorded in the redo log. The redo log is saved from memory to disk
with each committed database transaction. After a power failure, you can restart the
database as you would with any disk-based database. It then returns to its last consistent state by
replaying the redo log since the last savepoints.
Although savepoints and log writing protect your data against power failures, savepoints do not help if the persistent storage itself is damaged. To protect against data loss because of disk failures, backups are required. Backups save the payload (the actual data) of the data area and log area to different locations.
Types of Back-ups:
1.Data Backup
1) Full or complete Backup
2) Delta Backup
- Differential Backup
- Incremental Backup
3) Storage Snapshot
Destinations for Backups :
You can specify whether data and log backups are written to the file system (see SAP Note1820529 ), or using third-party backup tools (see SAP Note 1730932 ). The BACKINT software development kit (SDK) for the SAP HANA interface performs all the actions needed to write the backup data to external storage. The backup tools communicate directly with the SAPHANA database through the BACKINT SDK for the SAP HANA interface.
BACKINT
SDK for SAP HANA
BACKINT SDK for SAP HANA is an application programming interface
(API) that can be implemented by a third-party backup agent. It has the
following features:
● It provides
functions for backup, recovery, query, and delete.
● The third-party
backup agent runs on the SAP HANA server and communicates with the third-party
backup server.
● Backups are
transferred through pipes.
● It has full
integration with SAP HANA studio (configuration and execution of backups to BACKINT).
·
It can be configured for data backups and
for log backups.
Note:
SAP certification is required for
BACKINT SDK for SAP HANA implementations by third-party vendors.
Backup
of Multitenant Database Containers :
·
Points to Note :
·
Backups
can only be created when
SAP HANA is online. All the configured SAP HANA services must be
running.
·
While backups are being created, the
impact on system performance is negligible, and users can continue to work normally.
·
The system database plays a central
role. It can initiate backups of both the system database itself and individual tenant databases.
· A tenant database can create its own backups without the need to connect through the system database using onlyHana Cockpit (but not in Studio)
·
System database and tenant
databases have their own backup catalogs.
·
Backup and recovery always apply
to the whole database. You cannot back up and recover individual database
objects.
·
SAP HANA
backups created with release 1.0 SPS10 or newer can be used to recover to SAP HANA 2.0.
·
A backup of an SAP HANA
single-container system can only be recovered to a tenant database.
·
A backup of an SAP HANA
single-container system cannot be recovered to a system database.
Each
backup file name contains the following elements:
<<path>/<prefix>_<suffix>>.
·
The <path>
is optional. If no complete path is
specified, the default backup location is used.
· You can specify a <prefix> for the backup file name or you can use the prefix proposed by the system.
· The system adds a unique <suffix> to each backup file name that indicates the volume ID and the partition ID.
Ex:
HEP_HANA_FULL_HEP_DB_2021_04_27:02:00_databackup_2_4
$DATETIME ( DATE TIME)
$SUFFIX ( Default value as it come _databackup_ *)
Example:
Below is an example of a set of backups from one data backup.
</backup/data/COMPLETE_DATA_BACKUP_databackup_0_1>
</backup/data/COMPLETE_DATA_BACKUP_databackup_1_1>
</backup/data/COMPLETE_DATA_BACKUP_databackup_2_1>
In the above example, the <path> is </backup/data/>, the <prefix> is <COMPLETE_DATA_BACKUP>. <databackup_0_1> is the suffix, which is automatically added by the system. In the suffix, <0> is the volume ID, and <1> is the partition ID
BACKINT
location : /usr/sap/SID/SYS/global/hdb/backint/DB_SID/ can’t be changed
Log File Location “ /log
The default backup destination can only be changed for file-based backups.Backups made using third-party tools always use the destination /usr/sap/<SID>/SYS/global/hdb/backint. Because of this, you cannot change the backup destination for third-party tools.
Performing Backups Using SAP HANA Cockpit
1.In the SAP HANA cockpit, choose Manage
database backups under DB Administration.
2. To open the backup settings page, choose the Create Backup button at the top of the backup catalog.
● Differential Data
Backup
● Incremental Data
Backup
The
SAP HANA Cockpit uses the time stamp for the backup file prefix by default.
The
default location shows the path specified in global.ini under the backup
parameter
basepath_databackup
.
5. Once you have
started the backup, the progress is displayed.
Overview
of Backup Operations
Once you have started the backup, the progress is displayed. When the backup is finished, the backup details are shown.
You can cancel a running data backup from
the progress details screen.
SYSTEM DB:
TENANT DB:
Overview of Back-ups:
Performing
a Data Backup Using SAP HANA Studio
1. In
the Navigator view, select the system that you want to back up.
2. From
the context menu, choose Back Up .
3. Select
the type of data backup from one of the following:
● Complete Data Backup
● Differential Data Backup
● Incremental Data Backup
4. Specify
the location (directory) and the backup file prefix to use, and choose Next
The default location shows the path specified in global.ini
under the basepath_databackup backup
parameter.
5. When
all the settings are correct, choose Finish . The backup then starts. The
progress of the backup is shown for all types of services (for example, the
name server, and indexservers).When all the volumes have been backed up, a
confirmation message display.
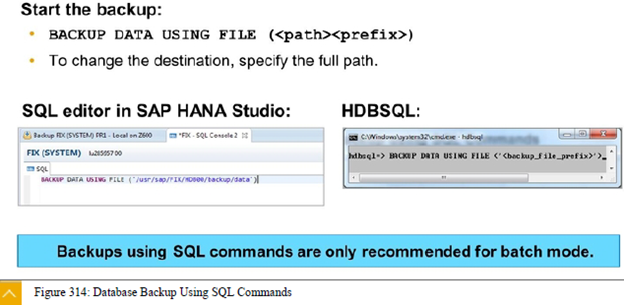
You
can enter SQL commands either by using the SQL editor in SAP HANA studio, or by
using the hdbsql program on the command line
Scheduling Backups Using SAP HANA Cockpit
Note:
-
SAP
HANA cockpit 2.0 cannot schedule backups for SAP HANA 1.0 databases.
- Currently snapshots cannot be scheduled.
Schedule Data Settings:
● Select the general
data backup settings:
- Backup Type
- Destination Type
- Backup Prefix
- Backup Destination
● Specify the proper
schedule data settings:
- Schedule Name
- Start of Schedule
- Recurrence pattern
- Execution time (in UTC time)
Note :
To transition from SAP HANA
1.0 to SAP HANA 2.0, note the following:
● Backup schedules created with SAP HANA cockpit 1.0 are not compatible with SAP HANA cockpit 2.0.
● Before you upgrade from SAP HANA 1.0 to SAP HANA 2.0, use the SAP HANA cockpit 1.0 to delete all the backup schedules created with SAP HANA 1.0.
● After you
upgrade to SAP HANA 2.0, create new backup schedules.
Enable
the Job Scheduler
The
XS job scheduler has to be activated for the system database and each tenant
database.A backup of a tenant database must be scheduled through the tenant
database itself. A backup of a tenant database cannot be scheduled through the
system database.
For
the system database, the XS scheduler must be enabled in the nameserver.ini
file. To enable the XS scheduler, you can use the following SQL statement:.
Scheduling the jobs using DBACOCKPIT
To start the DBA Cockpit, use transaction code DBACOCKPIT.
Performing Scheduling
To schedule an action, proceed as follows:
1. To
open the DBA Planning Calendar, in the DBA Cockpit, choose Jobs → DBA Planning Calendar
.
2. To
create a new action, perform one of the following:
● Double-click
a calendar row.
● Select
a calendar cell and choose Add.
● Move
an action from the Action Pad to a calendar cell in the future. You can also
move actions to reschedule them.
To copy an action, hold down the Ctrl key while dragging.
3. Specify
the following action details:
● Planned
Start: Specify the start date and time of the action.
● Action
Parameters: If different from the default, specify the location and prefix for
the file.
● Recurrence:
Specify when the action will be repeated or if it will be executed only once.
Multistreaming Data Backups with Third-Party Backup Tools
To configure the number of
parallel streams, use the parallel_data_backup_backint_channels.ini file
parameter (default: 1, max: 32).
During recovery, the number of streams used is the same as during backup. This is
independent
of the current setting of the parameter.
Configuring a Log Area Backup
A log is written to Log-Buffers in-memory.
If
a Log-Buffer becomes full or a commit entry is written, the Log-Buffer is
written to the assigned log volume.
The
log is finally written into log segments, where multiple Log-Buffers can be
combined.
You can find many log files
as log segments (1 GB) on the log volume.
Overwrite mode is as follows:
log_mode
= overwrite.
Note:
The overwrite mode, log_mode = overwrite, is not recommended for production systems.With log_mode = overwrite, no point-in-time recovery is possible. For recovery, only data backups are used; the logs are not used.
To Recover the database to a specific data backup recovery option is the only option that can be selected.
Normal
mode is as follows: log_mode = normal (default). The features of normal mode are as follows:
● Keeps log segments
until backup
● Automatic log
backup available (time-based or when segment is full)
Ex: 15 min or 1 GB of size
● Log backup
directory configured with parameter basepath_logbackup
Note:
After installation, SAP HANA temporarily runs in overwrite log mode. After you create the first full data backup, SAP HANA automatically switches to the default normal log mode.
Note:
Backups made using third-party tools always use the destination: /usr/sap/<SID>/SYS/global/hdb/backing. Can’t be changed.
Log segments in the log area are only released for overwrite after a successful log backup. In some situations, there can be a delay in releasing log segments because they are waiting to be backed up. As a result of this delay, the log area can grow. If the log segments cannot be backed up and released faster than the log area is growing, the log area can become even more full.
The maximum size of the
log segments to be processed by a single backup operation is defined by the
parameter max_log_backup_size in the backup section of the global.ini file. The
default value is 16. This means that one backup operation
creates log backups with a maximum size of 16GB.


























Comments
Post a Comment