Interview Questions 2
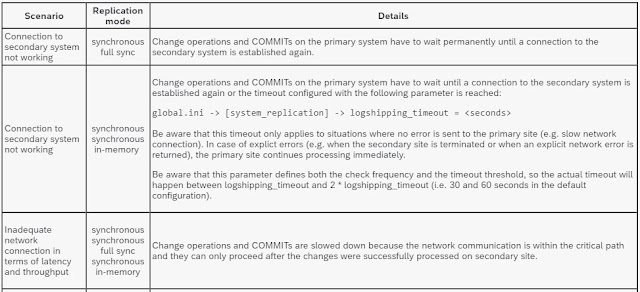
1. Can problems with system replication impact the performance on the primary system ? 2. Is it supported to set up a replication scenario between systems with different hardware ? Yes, it is possible to set up replication between systems that differ in terms of hardware (e.g. different manufacturer, different memory sizes, different number of CPUs). From a system replication perspective you only need to make sure that the number of hosts is identical on all sites and that every service has a partner on all sites. 3. Is it supported to set up a replication scenario between systems with a different SAP HANA patch level ? It is allowed to use different SAP HANA patch levels in a replication scenario as long as the patch level of the replicated system is not lower than the patch level of the primary system. It is also allowed that the replicated system is on a higher SPS level than the primary system. This possibility can be used for near-zero downtime upgrad...
